Quick facts:
- 1 in 20 (just over 1.3 million) Australians are living with diabetes
- Almost 1 in 5 Australians aged 80–84 are living with diabetes
- Diabetes is 1.3 times as common in males compared to females
For immediate first aid treatment for Hypoglycaemia, follow these steps:
- If unconscious – check airways, breathing and pulse
- Seek medical help immediately
- If conscious – feed patient a sugary drink and water
- When fully conscious – feed patient a sandwich or fruit
- Seek medical advice following a hypoglycaemic episode
See more in-depth treatment steps and a helpful free resource here.
Read on to learn more about Hypoglycaemia, and how to prevent and manage it.
Explore this blog:
- What is Hypoglycaemia?
- Low blood sugar level symptoms
- Hypoglycaemic episode prevention
- First aid steps
- Video explanation
What is Hypoglycaemia?
Hypoglycaemia (spelled Hypoglycemia in the US) is when blood sugar (glucose) levels drop too low (lower than 4 mmol/L). This can happen to people with diabetes when they:
- miss a meal or snack
- exercise more than usual without adjusting their insulin or other diabetes medications
- drink alcohol
- take certain diabetes medications
Low blood sugar level symptoms
A diabetic can suffer from low blood sugar and even become unconscious very quickly. You need to be able to recognise the symptoms of hypoglycemia and know how to treat it.
The most common symptom of low blood sugar is feeling shaky. Other symptoms may include sweating, pale skin, anxiety, dizziness, headache, heart palpitations, and hunger.
Hypoglycaemic Episode Prevention
Preventative measures for hypoglycaemic episodes include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet – Individuals with hypoglycaemia should eat regular meals and snacks that include carbohydrates and protein to help maintain their blood sugar levels. They should also avoid skipping meals or eating large amounts of sugary foods, which can cause their blood sugar levels to fluctuate.
- Regular exercise – helps maintain stable blood sugar levels by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin.
- Proper medication management – individuals should always follow their healthcare provider’s instructions for medication management, including dosage and timing, to help prevent hypoglycaemic episodes.
By taking these preventative measures, individuals can better manage their hypoglycaemia and reduce the risk of experiencing a hypoglycaemic episode.
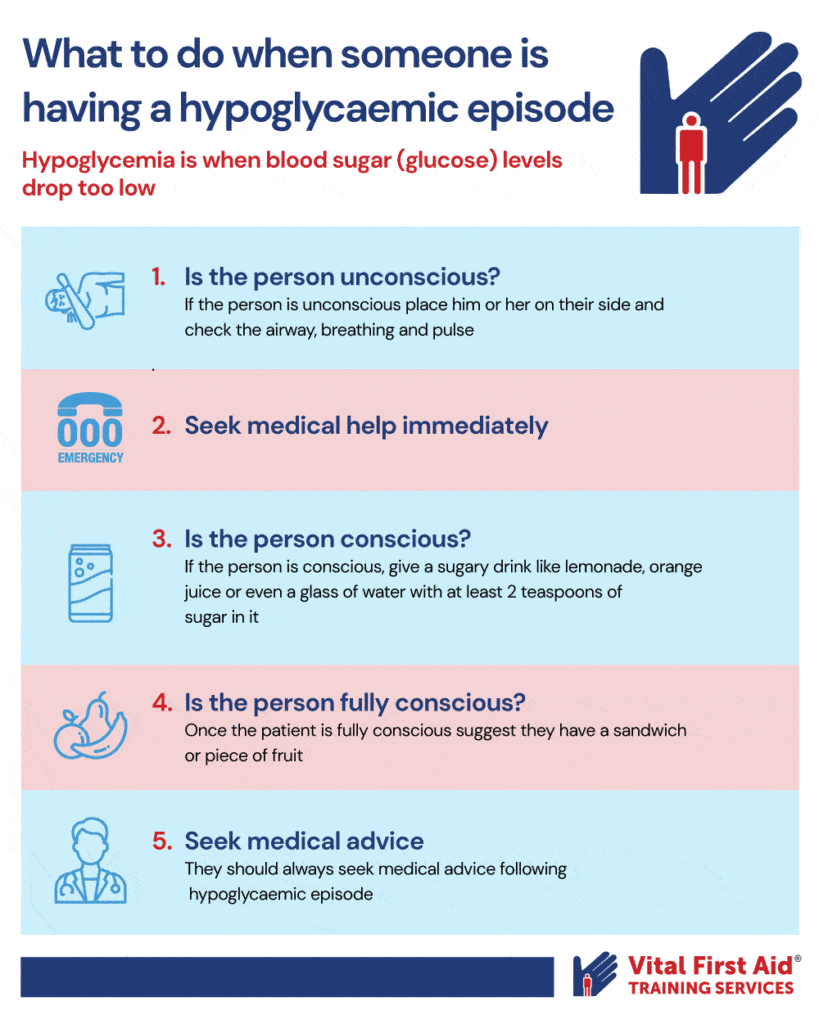
What to do when someone is having a hypoglycaemic episode
1. If the person is unconscious place him or her on their side and check the airway, breathing and pulse.
2. Seek medical help immediately.
3. If the person is conscious, give a sugary drink like lemonade, orange juice or even a glass of water with at least 2 teaspoons of sugar in it.
4. Once the patient is fully conscious suggest they have a sandwich or piece of fruit
5. They should always seek medical advice following a hypoglycaemic episode
For more information about dealing with hypoglycaemia and other aspects of first aid please book into a HLTAID003 Provide First Aid course soon…
Courses are available throughout Sydney, Newcastle and the Central Coast.
Sources: