The Vital Facts
- Injuring the eye is a primary reason for partial blindness in a single eye.
- Falls, assaults, and transportation incidents are the primary causes of eye-related hospitalisations.
- Eye injuries are more prevalent in males, especially among working-age individuals.
Just thinking about an eye injury is enough to make most people squeamish. Whether it’s putting in a contact lens or fishing out a stubborn eyelash, touching our eyes is often an uncomfortable experience.
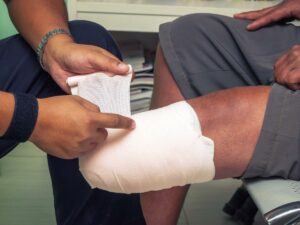
Despite your feelings about them, knowing how to provide first aid for eye injuries is essential. Like any injury, there is a correct process to follow, and knowing it is the best way to prevent losing your eye or your vision in an emergency.
Read the following guide to learn how to provide first aid for eye injuries.
Here’s a summary of what you’ll find in this guide:
- What is considered an eye injury?
- What isn’t considered an eye injury?
- Eye injuries resulting from chemical burns
- Eye injuries resulting from small foreign objects
- Eye injuries resulting from large foreign objects
- Eye injuries resulting from lacerations or punctures
- Eye injuries resulting from impacts
What is Considered an Eye Injury?
For this guide, eye injuries are caused by sudden traumas from an outside source, whether that be a chemical burn, an object, or an impact. Treatment of eye injuries focuses more on mitigation and pain relief than on diagnosis.
What isn’t Considered an Eye Injury?
There are some things that can cause eye irritation or pain that aren’t classed as injuries for the purposes of first aid.
For example, eye irritation from allergies, bacterial or viral infections like conjunctivitis, or dry eyes are not emergency situations. Simply visit a pharmacist or your GP for a diagnosis and treatment.
Eye Injuries Resulting from Chemical Burns
One of the most common eye injuries in a household is chemical burns. Many cleaning products can irritate or outright damage your eye. Some of the most common, and worst, are:
- Drain cleaner
- Bleach
- Oven cleaner
- Polishes
- Paint thinners
While the worst injuries are a result of direct splashing to the eye, people often mistakenly rub their eyes with hands that still have traces of chemicals, which can also cause injury.
How to Treat a Chemical Burn Eye Injury
Here are the steps to for providing first aid to a chemical burn eye injury:
- Keep the affected eye open. While your instinct will be to close it to stop the pain, this can trap chemicals and push them further into or around the eye. If you are wearing contact lenses, remove them immediately.
- Flush the eye under cool water for at least 15-20 minutes. As with regular burn injuries, make sure the water is not ice cold. If it is difficult to target the eye, run water over your face while holding the eye open.
- Immediately seek medical assistance or advice. Do not attempt to drive yourself if your vision or ability to keep your eyes open is impacted. Also, take mental notes about what the chemical was, how much entered your eye and how long it has been since the injury occured. All these details will help medical professionals treat you.
Important Note
It can be very difficult to assess the severity of chemical burns. Just because a burn isn’t very painful (alkaline burns often aren’t) doesn’t mean it isn’t serious. Many complications can occur after the fact and receiving qualified advice or an eye examination is the best way to ensure you don’t sustain unnecessary damage.
Eye Injuries Resulting from Small Foreign Objects
Small foreign objects are another extremely common eye injury cause. For kids playing outside during summer or adults who enjoy camping in the great outdoors, things like sand, dirt, and plant matter can easily find their way into our eyes.
These small foreign objects can usually be easily wiped out, or make their way out on their own. However, sometimes they can become lodged and cause irritation and pain.
How to Treat Eye Injuries Resulting from Small Foreign Objects
Here are the steps for providing first aid to a small foreign object eye injury:
- Try to let your eye naturally flush it out. Blink and roll your eyes to see if that loosens or removes the particle. Your eye may tear up, which is its natural way of flushing out particles. Do not rub your eye, as this can push the particle further into the surface of your eye, making it more difficult to remove.
- If your eye can’t flush it out naturally, use saline solution or cool water to manually flush your eye.
- If this doesn’t work, see your doctor. They’ll be able to attempt to remove it, or they’ll be able to refer you to a specialist.
Important Note
If you suspect the foreign object is a human-made material, such as plastic, metal, paint or glass, seek out medical attention immediately. These materials are more coarse and won’t naturally break down or loosen over time. They may actually become more embedded and can contaminate your eye.
Eye Injuries Resulting from Large Foreign Objects
If a large foreign object becomes embedded in your eye, this is much more serious and requires immediate action. These injuries often occur when children accidentally have sticks lodged in their eyes while playing, or when people on a worksite are injured by nails or bolts.
How to Treat Eye Injuries Resulting from Large Foreign Objects
Here are the steps for providing first aid for small foreign object eye injury:
- Do not remove the object! Removing a large embedded object can cause severe damage.
- Call an ambulance immediately. If you are the one who has suffered the injury, do not drive yourself to the hospital.
- If the object is small enough that the eye can still close, cover both eyes with sterile dressings. If the object protrudes through the eyelids, tape a sterile paper cup or similar object over the injured eye, and then cover the other eye with a sterile dressing. It is important to cover both eyes because you want to limit the affected person’s eye movement, and leaving one eye uncovered may tempt them to look around, which will cause both eyes to move.
- Advise the affected person to limit their eye movement as much as possible.
Important Note
Due to how confronting a large foreign object being embedded in the eye can be, it is very important to keep the injured person calm. They may want to remove the object, or try to resist having both eyes covered. Keeping them immobile and as relaxed as possible is essential.
It’s also important to be aware of signs the sufferer is going into shock. In an embedded eye injury, the cause of the injury continues to affect the sufferer, so they can go into shock even after the initial penetration.
Eye Injuries Resulting from Lacerations or Punctures
This is another common eye injury that requires first aid. In these cases, the eye is lacerated or punctured by an object, but the object doesn’t stay lodged in the eye. These can range from a small scratch with a fingernail to a deep cut caused by a sharp object.
Depending on the severity of the injury, you may need to provide first aid differently. Where the eye has been lacerated or punctured can also be a factor.
How to Treat Eye Injuries Resulting from Lacerations or Punctures
Here are the steps for providing first aid for a laceration or puncture eye injury:
- If the wound is very minor, you can simply observe ongoing symptoms and visit a GP for advice.
- If the wound is more severe, you should seek medical advice immediately. Infection risks are far more serious in the eye than on other areas of the body where cuts or punctures can occur.
- Do not rub or rinse the eye. Simply cover it with a sterile dressing and limit movement of the eye.
- Resist the urge to take any aspirin, ibuprofen or other anti-inflammatory medication as these thin the blood and can worsen bleeding.
Eye Injuries Resulting from Impacts
Impacts to the eye are extremely common in sport and as a consequence of fighting. However, while most people think of a black eye or a few burst blood vessels, impact eye injuries can be much more serious.
The first problem is that head injuries can often lead to concussions, which can impair vision. This means serious eye damage will not be initially recognised because it is assumed to be a symptom of the concussion.
The second problem is that other than keeping the eye immobilised, serious eye injuries can’t be treated at home. If you suspect any of the following symptoms, seek emergency care.
Symptoms of a Serious Impact Eye Injury
Symptoms of a serious impact eye injury can present in many different ways:
- Double, blurred, partial or otherwise changed vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Limited ability to move the eye in different directions
- Painful eye movement
- Severe pain in the eyeball
- Numbness around the eye
- A change in pupil size or shape, or pupils of different sizes
- Excessive blood collecting in the white (sclera) section of the eye
- Blood in the coloured (iris) section of the eye.
- Feeling like there is something in your eye
- Deformity of the eye socket bone that isn’t caused by swelling alone.
- Abnormal upper eyelid movement
Any of these symptoms can be a sign of more severe injury.
Have You Considered a First Aid Course?
Of all the emergency situations you can encounter, needing to provide first aid for eye injuries can be one of the most stressful. The sufferers of the injury are often conscious and in distress, and fear of causing permanent vision loss by making a mistake can often cloud your judgement.
The best way to take the stress out of providing first aid is by taking a first aid course.
Vital First Aid provides realistic training that will keep you calm and confident about your knowledge when faced with a stressful situation, such as an eye injury.
To find out more about our courses, visit our website. Or, if you are ready to sign up for a course, get in touch today.